IT Asset Management Lifecycle
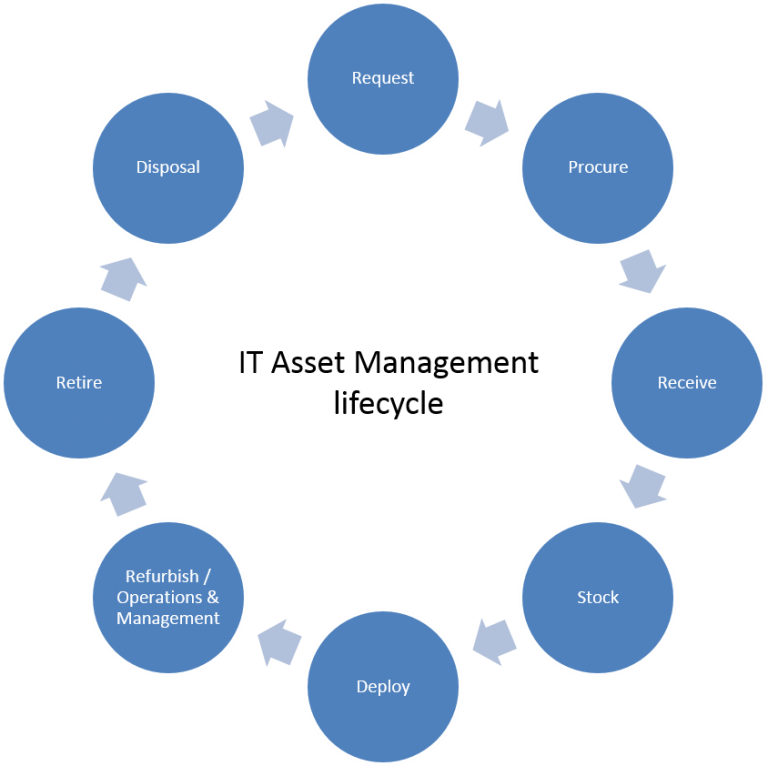
Activities
IT Inventory and Asset Practices – Define and establish how assets will be managed throughout their lifecycle (includes identifying optimal lifecycle).
Capture and Maintain Inventory Information – Maintain the data required to support the procurement process and various other information needs (technical, financial, legal, etc.) and to ensure that assets are managed. This includes recording. Tracking, reporting, and accounting for and updating resource information. Reconciliation with vendor records is also included.
Maintain IT Asset Information – Addresses those activities that allow an enterprise to properly finance assets for business planning and financial record keeping.
Administer License or Lease – Tracks the contracting arrangements for assets, and ensures that all terms and options are understood and maximized to the benefit of the business. This
step is particularly challenging with the availability of multiple software license alternatives as well as methods for distribution of software across the enterprise.
Maintain Warehouse Inventory – takes over from the procurement receipt process and provides any asset tagging that is required by the enterprise. Also provided is inventory information, and “change management” notification of installations. Some enterprises keep assets in stock for immediate distribution (must be cautious of customer satisfaction issues if safety stock is held too long) to ensures availability of spares or spare parts for critical assets and to assure product availability when necessary within shorter periods than standard vendor lead times.
Charge-back Administration – The cost of charging assets and support services back to business unit cost centers. Included in the charge-back are personnel costs and license and maintenance fees.
Technology Portfolio Financial Planning – The cost of performing financial analyses on the desktop portfolio to support planning, budgeting, and ad hoc studies.
Physical Property Protection – The cost of maintaining insurance coverage on assets, replacement cost, and developing and implementing processes for handling losses.
Security – Includes policy development, assurance (monitoring), and enforcement. Costs include theft and impact of breaches.
